Lung cancer basically falls into two categories: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.
Lung cancer basically falls into two categories: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.
Small cell lung cancer is also of two types: small cell carcinoma and combined small cell carcinoma.
These two types of small cell lung cancers include various types of cells which grow and spread in different ways.
These cancers are named according to the types of cells originated in the cancer and their appearance when observed under the microscope.
Tobacco smoking is a major risk factor for small cell lung cancer
Cigarette smoking is the main risk factor for lung cancer. However, small cell lung cancer can be due to:
- Smoking cigarettes, pipes or cigars;
- Exposure to secondhand smoke;
- Exposure to radon or asbestos increases risk of small cell lung cancer by 9 times.
Coughing, chest pain, shortness of breathe – possible signs of lung cancer
Consult your doctor if you have any of the following problems:
- Coughing that won’t go away;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Severe chest pain that won’t go away and made worse by deep breathing;
- Coughing up blood;
- Hoarseness;
- Swelling of your neck and face;
- Suppressing appetite;
- Weight loss for no definite reason’
- Unusual tiredness.
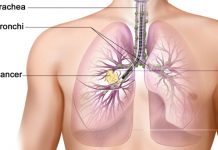
Lung cancer spreads in the body in three different ways:
- Cancer attacks the surrounding normal tissues.
- Cancer attacks your lymph system and spreads to other body parts through the lymph vessels.
- Cancer attacks the veins and capillaries and spreads to other body parts through the blood.
Small cell lung cancer progresses in three stages:
- Limited stage small cell lung cancer, in which cancer is found in only one lung, tissues between lungs and the nearby lymph nodes.
- Extensive small cell lung cancer, in which cancer spreads outside of the lungs and also to other parts of body.
- Recurrent small cell lung cancer, i.e. cancer recurs after it has been treated.
The most effective cancer treatment for treating small cell lung cancer is chemotherapy, either alone or in combination with radiation therapy. Based on the stage of your cancer, your doctor will prescribe chemotherapy drugs or combination drugs.
Surgery is suggested for those whose cancer is detected during the early stages, i.e. cancer is confined only to the lungs without any spread to the lymph nodes.
The most important way to treat lung cancer is to avoid smoking. There are plenty of products that can help you to quit. They include: nicotine gum, nicotine patches, medicated nicotine inhalers or sprays, and oral medications. Behavioral therapy and group therapy can also help to give up smoking.