Signs and Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Colorectal cancer or colon cancer may not cause any serious symptoms in early stages, but there are few signs which are raise suspicion.
- Change in bowel habits like constipation or diarrhoea or change in the stool consistency.
- Narrow, pencil like thin stools
- Rectal bleeding or blood seen in the stools.
- Persistent abdominal discomfort such as gas, cramps or pain.
- Feeling bowel does not empty completely
- Unexplained weight loss
- Constant fatigue.
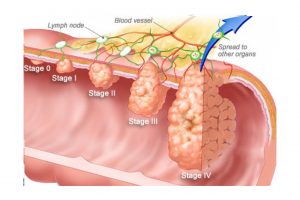
4 Stages of Colorectal Cancer
Removing tumour or polyp (bulged tissue from the surface of an organ) during regular colonoscopy is the best way to prevent colorectal cancer. Make sure that you are visiting a gastroenterologist regularly; getting colonoscopy done for every 2 years is one of the best ways to prevent colon cancer. Colorectal cancer or colon cancer has four distinct stages; each stage has different treatment procedures and has at least 5 years survival rates. Here are different stages of colon cancer.
Stage 0
Stage 0 is the earliest stage of colon cancer. The cancer is present only at the lining or mucosa of the rectum or colon. If you find polyp during the colonoscopy, it is better to remove. The cancer may progress and increases the growth which can leads to later stages of colorectal cancer.
Stage 1
Cells that line the colon are very active, constantly dividing and creating buds, know as polyps. Most polyps are small, benign growth that eventually stop growing.
Stage 2
A tiny percentages of these polyps keep growing sometimes for ten years or more. Various genetic mutations can transform them into cancerous tumours.
Stage 3
As these tumours grow larger, they gather more mutations and begin to burrow deeper and deeper into the muscle wall that surrounds the colon.
Stage 4
Once the cancer invades the blood and lymp system, malignant cells can break off and spread to other organs, such as the liver, lungs and stomach.
How to Prevent Colon Cancer
Talk your doctor, discuss about the condition and know the risk factors of colon cancer. People with IBD (inflammatory bowel syndrome) are at the greater risk of developing colorectal cancer. So, take extra care of yourself, if you are having IBD. Get in touch with your gastroenterologist and take continuous colonoscopy appointments, which can help you in eliminating polyps and checks your colon health. Sometimes you may feel little embarrassment or discomfort during the process of colonoscopy but it is very important part to check your colon health. It is good for people who crossed 50 years of age should be screened for colon cancer.